AI model recognizes fatty liver based on X-ray images
Fatty liver disease, which affects around one in four people worldwide, can lead to serious complications such as cirrhosis or liver cancer if left untreated. While standard diagnostics such as ultrasound, CT or MRI require expensive specialist equipment, chest X-rays offer a cost-effective alternative with low radiation exposure. Although primarily used for the lungs and heart, these images also show parts of the liver, which makes it possible to detect fatty liver. This connection has hardly been researched to date.
A team led by Associate Professor Sawako Uchida-Kobayashi and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda from Osaka Metropolitan University developed an AI model that identifies fatty liver disease from chest X-ray images. In a retrospective study, 6,599 X-ray images of 4,414 patients were analyzed to train the model, which uses controlled attenuation parameters (CAP). The model achieved high accuracy with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.82 to 0.83.
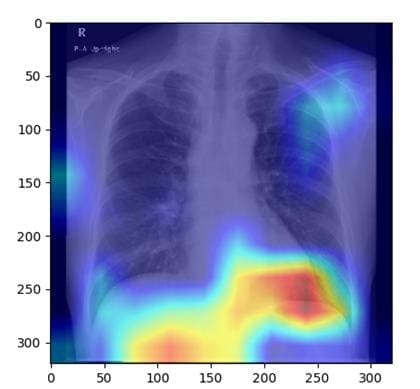
The method could significantly improve the early diagnosis of fatty liver disease, as X-rays are widely available and inexpensive. The researchers hope that AI-assisted diagnostics will soon be used in clinical practice to facilitate the detection and treatment of this disease.
Original Paper:
Read also:
Fatty liver during pregnancy can increase the risk of premature birth – MedLabPortal
Editorial office: X-Press Journalistenb├╝ro GbR
Gender note. The personal designations used in this text always refer equally to female, male and diverse persons. Double/triple references and gendered designations are avoided for the sake of better readability ected.




