New study identifies CISD1 as a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis and therapy
Despite medical advances, cancer remains the leading cause of death worldwide, highlighting the need for ongoing research to identify reliable biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and treatment. A study published in the journal Genes & Diseases by researchers from Louisiana State University, Tulane University, University of Florida, University of Texas Medical Branch and other partners provides the first comprehensive bioinformatic analysis of the role of the CISD1 gene in various types of cancer. The study shows that CISD1 could be a versatile biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis and immunotherapy.
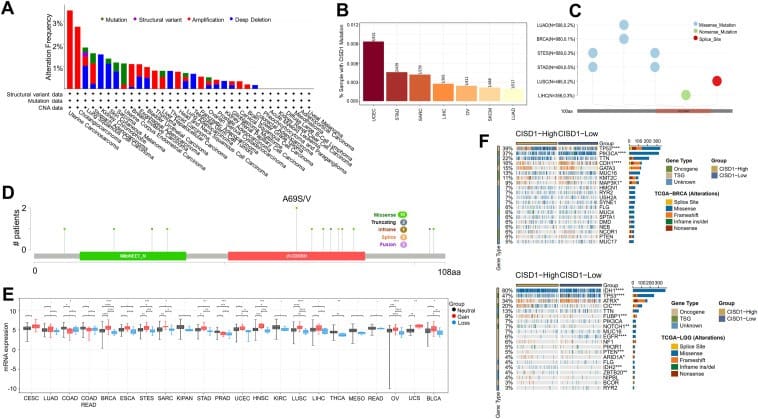
The analysis is based on data from public databases such as TCGA, GTEx, THPA, GEPIA2.0, SangerBox, cBioPortal, TIMER2.0, CAMOIP, DAVID, SRPLOT, and TISIDB. It shows significant changes in CISD1 expression at the transcriptional and translational level in numerous types of cancer. Mutations in the CISD1 gene, particularly at the A69S/V position in the zf-CDGSH domain, have been identified in several cancer types and suggest a role in tumorigenesis and progression. High CISD1 expression correlates with poor clinical outcomes, including low survival rates and increased risk of death. In addition, CISD1 shows a positive correlation with stem cell indices, indicating a promotion of stem cell-like properties in cancer cells, which can increase tumor aggressiveness and therapy resistance.
The study also shows that CISD1 plays a central role in cellular bioenergetics and is linked to the mutational burden and microsatellite instability of the tumor , which also causes a worse prognosis. CISD1 expression was altered in immunotherapy patients, with tumors with high CISD1 expression having elevated levels of immune checkpoint proteins. These proteins are important targets for immune checkpoint blockade, positioning CISD1 as a potential predictor of the success of such therapies.
Despite its predominantly tumor-promoting role in most cancers, CISD1 showed downregulated expression in six cancer types, suggesting tumor-suppressive functions. The researchers see CISD1 as a potential therapeutic target, for example through strategies that modulate the iron-sulfur cluster of the gene or its expression. Limitations of the study lie in the lack of experimental validation and possible biases due to heterogeneous data sets.
The results underpin the potential of CISD1 as a versatile biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis and immunotherapy in cancer. They form a basis for further research to deepen the biological functions of CISD1 and to develop new therapeutic approaches.
Original Paper:
Editor: X-Press Journalistenbû¥ro GbR
Gender Notice. The personal designations used in this text always refer equally to female, male and diverse persons. Double/triple naming and gendered designations are used for better readability. ected.




