Mirror image amino acid specifically inhibits cancer cells
Research teams from the Universities of Marburg and Geneva have discovered that the mirror-image amino acid D-cysteine can specifically inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells. The results, published in the journal Nature Metabolism, shed light on the underlying molecular mechanisms and show possible approaches for tumor therapy.
In contrast to the natural amino acid L-cysteine, which is essential for protein synthesis, D-cysteine cannot be used to build protein molecules. The researchers found that D-cysteine acts in tumor cells that have high levels of a specific cysteine transporter in the cell membrane. This transporter, which normally absorbs L-cysteine and thus promotes tumor growth, also enables the uptake of D-cysteine, which, however, triggers toxic effects in the cell.
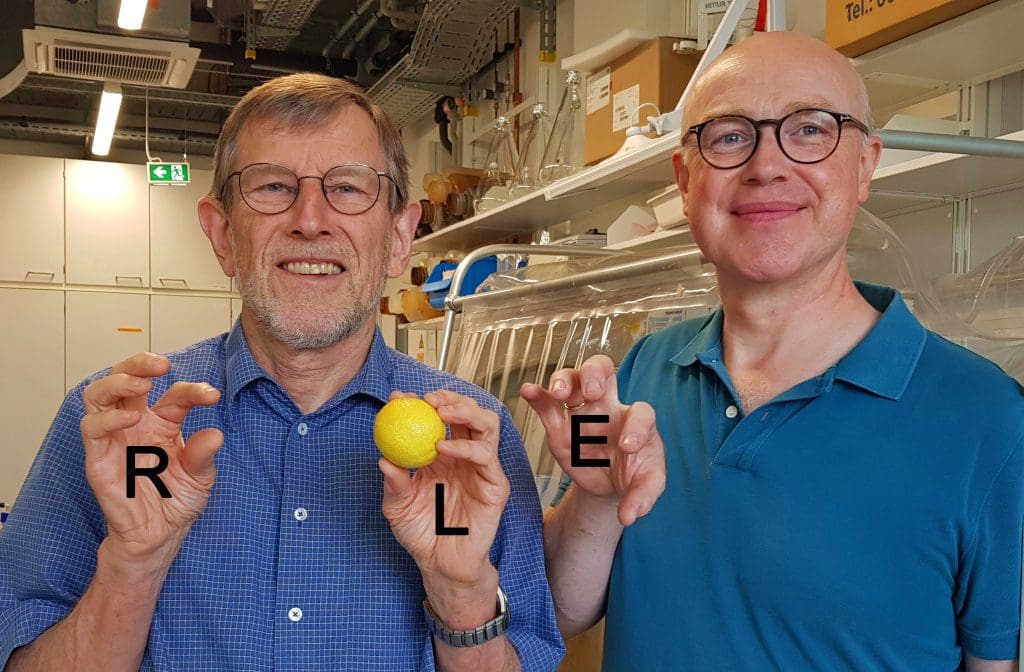
This is an example of how D-cysteine has a toxic effect in cells: Normally, the yellow sulphur is transferred from the left hand (L) to a recipient position in the enzyme (E). However, if the yellow sulphur is in the right hand (R), the distance to the receiver position is too great. As a result, the transmission reaction, which is vital for the cell, cannot take place and the cell dies. Photo: Carina Beimborn; Editing: Roland Lill.
The Marburg team, led by Prof. Roland Lill, an expert in iron-sulphur proteins, showed that D-cysteine blocks a key enzyme that incorporates sulphur from L-cysteine into iron-sulphur proteins. These proteins are essential for vital processes such as DNA synthesis. The mirror-image structure of D-cysteine prevents sulfur transfer because the sulfur cannot be transferred to the right place in the enzyme. This leads to a lack of functional iron-sulfur proteins, which causes the tumor cells to die.
Initial tests on mice in the Geneva laboratory confirmed that D-cysteine can significantly inhibit tumor growth. The results indicate a high potential for tumor therapy. The researchers now plan to further test the suitability of D-cysteine for clinical use in order to develop new approaches in cancer therapy.
Original Paper:
D-cysteine impairs tumour growth by inhibiting cysteine desulfurase NFS1 | Nature Metabolism
Editor: X-Press Journalistenb├╝ro GbR
Gender Notice. The personal designations used in this text always refer equally to female, male and diverse persons. Double/triple naming and gendered designations are used for better readability. ected.




